CCE 2018 Quals - VNC
09 Oct 2018지난 주 사이버공격방어대회 (CCE 2018) 에 일반방어팀으로 참가하였다.
예선 1번 문제는 캡쳐한 VNC 원격데스크탑 패킷을 분석하여 정보를 알아내는 것이다.
암호화가 안 되어있어서 와이어샤크에서 내용이 그대로 보였다.
1. 키보드와 클립보드
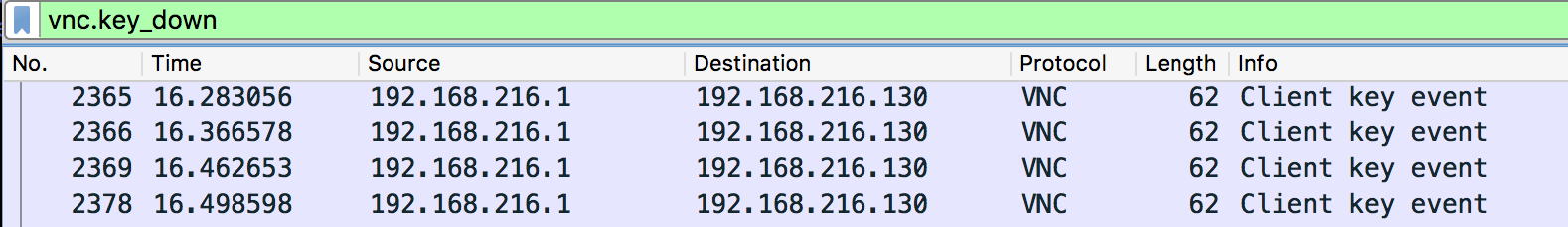
제일 눈에 띄는 키보드 패킷만 골라보면 클라이언트가 _Y0u_g)t_VNC 를 입력했음을 알 수 있다.
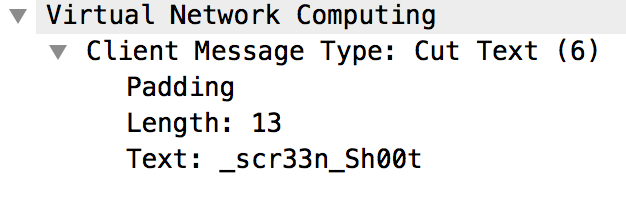
그 다음 클립보드를 통해 _scr33n_Sh00t를 붙여넣기했음을 알 수 있다.
둘 다 _ 로 시작하는 걸 보니 앞부분에 몇 글자가 더 있는 것 같다.
남은 부분은 화면상에 적혀있을 것이라고 짐작할 수 있다.
2. 화면
처음에는 https://github.com/sibson/vncdotool 를 고쳐서 쓰려고 했는데 패킷을 처리하는 부분하고 네트웍 레이어가 합쳐져 있어서 힘들어 보였다. 그래서 RFC 6143 을 참고하여 직접 FrameBufferUpdate 패킷을 디코딩했다.
패킷에서 팔레트 정보를 찾을 수 없어서 팔레트 숫자별로 랜덤한 색을 배정했다.
from PIL import Image
import zlib
import struct
def db(d):
return d[1:], struct.unpack('>B', d[:1])[0]
def dw(d):
return d[2:], struct.unpack('>H', d[:2])[0]
def dd(d):
return d[4:], struct.unpack('>I', d[:4])[0]
def color(f):
f, c = db(f)
return f, (c,)
# Run-length number
def number(f):
n = 0
while True:
f, byte = db(f)
if byte == 255:
n += 255
else:
n += byte + 1
break
return f, n
# Continuously decompress the zlib stream.
z = zlib.decompressobj()
# Draw the accumulated "diffs" sent from the server.
I = Image.new('L', (1713,927))
counter = 0
# A rectangular part of the screen.
# Pixels are filled left-to-right, top-to-bottom.
class Tile(object):
def __init__(self, I, tx, ty, tw, th):
self.I = I
self.tx = tx
self.ty = ty
self.tw = tw
self.th = th
self.cx = 0
self.cy = 0
self.done = False
def put(self, color):
if self.done:
raise Exception('Tile size calc failed')
# Convert a palette index to a random number
# since we don't have the exact palette.
if len(color) == 1:
color = (color[0]*17 % 256,)
I.putpixel((self.tx + self.cx, self.ty + self.cy), color)
self.cx += 1
if self.cx == self.tw:
self.cx = 0
self.cy += 1
if self.cy == self.th:
self.done = True
def __repr__(self):
return 'Tile(%d %d %d %d)' % (self.tx, self.ty, self.tw, self.th)
def maketiles(x, y, w, h):
global I
tiles = []
tx = x
ty = y
while h > 0:
th = min(64, h)
h -= th
while w > 0:
tw = min(64, w)
w -= tw
tiles.append(Tile(I, tx, ty, tw, th))
tx += tw
tx = x
ty += th
return tiles
# Handle one frame buffer Rect.
def paste(x, y, w, h, f):
# Skip some frames before opening the Internet.
global counter
counter += 1
if counter < 110:
pass
tiles = maketiles(x, y, w, h)
for tile in tiles:
if len(f) == 0:
break
f, kind = db(f)
if kind == 128: # run-length
while not tile.done:
f, c = color(f)
f, n = number(f)
for _ in range(n):
tile.put(c)
elif kind == 1: # solid fill
f, c = color(f)
while not tile.done:
tile.put(c)
elif 2 <= kind and kind <= 16: # packed palette
palette = map(ord, f[:kind * 1])
f = f[kind * 1:]
if kind == 2:
m = (tile.tw+7)/8*tile.th
b = 1
elif kind == 3 or kind == 4:
m = (tile.tw+3)/4*tile.th
b = 2
else:
m = (tile.tw+1)/2*tile.th
b = 4
bytearr = map(ord, f[:m])
bitstrarr = map(lambda n: bin(n)[2:].rjust(8, '0'), bytearr)
bitstr = ''.join(bitstrarr)
f = f[m:]
for i in range(m):
pxstr = bitstr[:b]
bitstr = bitstr[b:]
c = (palette[int(pxstr, 2)],)
tile.put(c)
elif kind == 0:
while not tile.done:
f, c = color(f)
tile.put(c)
else:
raise Exception("Bad TRLE kind " + str(kind))
# Handle one FrameBufferUpdate packet.
def msg(d):
d, kind = db(d)
if kind != 0:
raise Exception("Not FramebufferUpdate")
d, pad = db(d)
d, count = dw(d)
for _ in range(count):
d, x = dw(d)
d, y = dw(d)
d, w = dw(d)
d, h = dw(d)
d, encoding = dd(d)
print 'FRAME x=%d y=%d w=%d h=%d encoding=%d' % (x, y, w, h, encoding),
if encoding == 0xffffff11: # -239
print 'Cursor pseudo'
d = d[w*h:] # pixels
d = d[(w+7)/8*h:] # mask
elif encoding == 0xffffff18: # -232 -- not in the RFC docs.
print 'Unknown'
elif encoding == 0xffffff21: # -223
print 'DesktopSize pseudo'
elif encoding == 16:
d, l = dd(d)
print 'ZRLE'
b = d[:l]
d = d[l:]
frame = z.decompress(b)
paste(x, y, w, h, frame)
else:
raise Exception("Unknown subencoding")
return d
# 1. Open prob.pcapng with Wireshark
# 2. Filter "tcp stream eq 0"
# 3. Select Server -> Client packets
# 4. Save the stream as binary file
with open('raw.bin') as f:
d = f.read()
# Skip handshake packets
d = d[0x4b:]
trial = 0
while len(d) > 0:
d = msg(d)
I.save('img/%03d.png' % trial)
trial += 1
그렇게 해서 아래 스크린샷을 얻었다.

3. 비밀번호
이제 비밀번호만 알아내면 된다.
VNC의 인증 프로토콜은 다음과 같다:
- 서버가 클라이언트에게 랜덤한 16바이트 챌린지를 준다.
- 클라이언트가 비밀번호와 챌린지를 넣고 정해진 방법에 따라 DES로 암호화한다.
- 암호화한 16바이트 결과를 서버에게 주면 서버가 이를 검증한다.
패킷 상에 서버가 보낸 메시지와 클라이언트가 보낸 메시지가 다 있으므로 brute force 를 통해 비밀번호를 알아낼 수 있다.
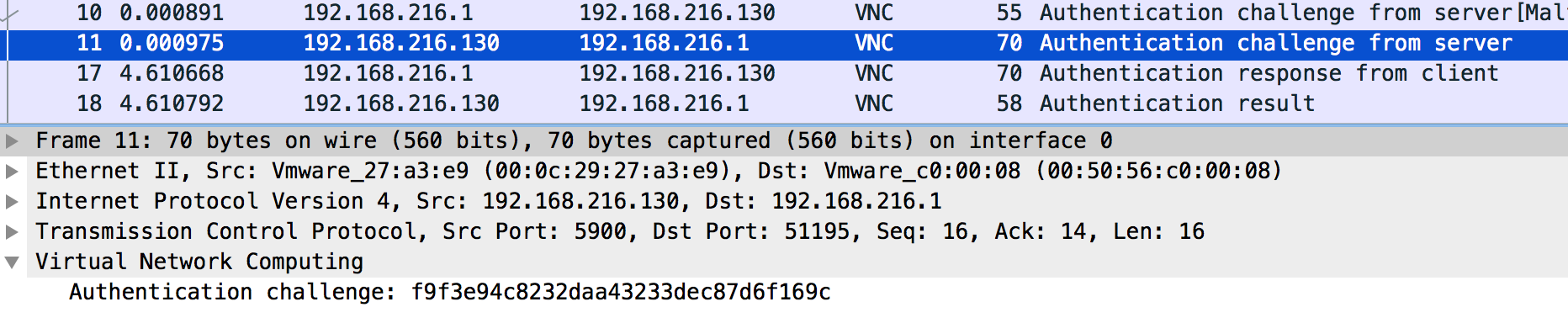
https://github.com/mitchellh/go-vnc 를 고쳐서 아래와 같은 프로그램을 만들어서 알파벳 4글자로 된 비밀번호를 찾을 수 있었다.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"crypto/des"
)
func reverseBits(b byte) byte {
var reverse = [256]int{
0, 128, 64, 192, 32, 160, 96, 224,
16, 144, 80, 208, 48, 176, 112, 240,
8, 136, 72, 200, 40, 168, 104, 232,
24, 152, 88, 216, 56, 184, 120, 248,
4, 132, 68, 196, 36, 164, 100, 228,
20, 148, 84, 212, 52, 180, 116, 244,
12, 140, 76, 204, 44, 172, 108, 236,
28, 156, 92, 220, 60, 188, 124, 252,
2, 130, 66, 194, 34, 162, 98, 226,
18, 146, 82, 210, 50, 178, 114, 242,
10, 138, 74, 202, 42, 170, 106, 234,
26, 154, 90, 218, 58, 186, 122, 250,
6, 134, 70, 198, 38, 166, 102, 230,
22, 150, 86, 214, 54, 182, 118, 246,
14, 142, 78, 206, 46, 174, 110, 238,
30, 158, 94, 222, 62, 190, 126, 254,
1, 129, 65, 193, 33, 161, 97, 225,
17, 145, 81, 209, 49, 177, 113, 241,
9, 137, 73, 201, 41, 169, 105, 233,
25, 153, 89, 217, 57, 185, 121, 249,
5, 133, 69, 197, 37, 165, 101, 229,
21, 149, 85, 213, 53, 181, 117, 245,
13, 141, 77, 205, 45, 173, 109, 237,
29, 157, 93, 221, 61, 189, 125, 253,
3, 131, 67, 195, 35, 163, 99, 227,
19, 147, 83, 211, 51, 179, 115, 243,
11, 139, 75, 203, 43, 171, 107, 235,
27, 155, 91, 219, 59, 187, 123, 251,
7, 135, 71, 199, 39, 167, 103, 231,
23, 151, 87, 215, 55, 183, 119, 247,
15, 143, 79, 207, 47, 175, 111, 239,
31, 159, 95, 223, 63, 191, 127, 255,
}
return byte(reverse[int(b)])
}
func encrypt(key string, bytes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
keyBytes := []byte{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}
if len(key) > 8 {
key = key[:8]
}
for i := 0; i < len(key); i++ {
keyBytes[i] = reverseBits(key[i])
}
block, err := des.NewCipher(keyBytes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
result1 := make([]byte, 8)
block.Encrypt(result1, bytes)
result2 := make([]byte, 8)
block.Encrypt(result2, bytes[8:])
crypted := append(result1, result2...)
return crypted, nil
}
func compareArrays(a []byte, b []byte) bool {
for i := 0; i < 16; i ++ {
if a[i] != b[i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func check(pw string) bool {
challenge := []byte{
249, 243, 233, 76 , 130, 50 , 218, 164, 50 , 51 , 222, 200, 125, 111, 22 , 156,
}
expected := []byte{
28 , 100, 110, 232, 209, 121, 9 , 225, 187, 25 , 0 , 239, 206, 111, 150, 26,
}
response, _ := encrypt(pw, challenge)
return compareArrays(expected, response)
}
func main() {
var pw string
arr := make([]byte, 8)
charset := []byte{
97 , 98 , 99 , 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115,
116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 ,
77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 ,
}
for a := 0; a < 52; a ++ {
fmt.Printf("a=%d\n", a)
arr[0] = charset[a]
for b := 0; b < 52; b ++ {
arr[1] = charset[b]
for c := 0; c < 52; c ++ {
arr[2] = charset[c]
for d := 0; d < 52; d ++ {
arr[3] = charset[d]
pw = string(arr)
ok := check(pw)
if ok {
fmt.Printf("%s", pw)
os.Exit(0)
}
}
}
}
}
}
찾은 비밀번호는 eovn 이다.
4. 정답
>>> import hashlib
>>> msg = 'eovn' + '_Y0u_g)t_VNC' + '_scr33n_Sh00t'
>>> hashlib.sha256(msg).hexdigest()
'43e5d9ec2d713cdea8665bcc86bf033137fe99076e1a027f101bc198c57414c4'
플래그는 CCE{43e5d9ec2d713cdea8665bcc86bf033137fe99076e1a027f101bc198c57414c4} 이다.